The Importance of Risk Monitoring in Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
In the complex and ever-evolving landscape of global finance, Anti-Money Laundering (AML) has emerged as a crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for financial institutions. The crux of AML efforts lies in identifying and mitigating the risks associated with money laundering activities. Risk monitoring plays a pivotal role in this endeavor, enabling organizations to detect, assess, and respond to potential threats in a timely and effective manner. This article explores the importance of risk monitoring in AML, shedding light on its significance, methodologies, and best practices.

Understanding AML and Its Significance
What is AML?
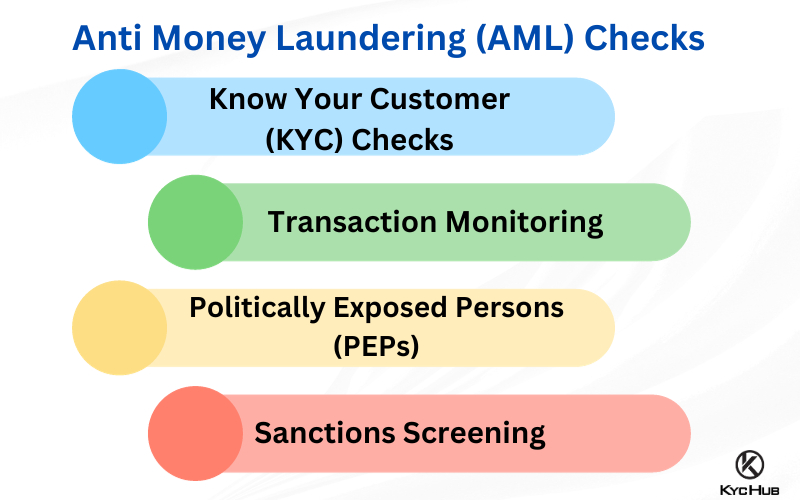
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) refers to a set of laws, regulations, and procedures aimed at preventing criminals from disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate income. AML processes involve a range of activities, including customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and reporting suspicious activities to regulatory authorities.
Why is AML Important?
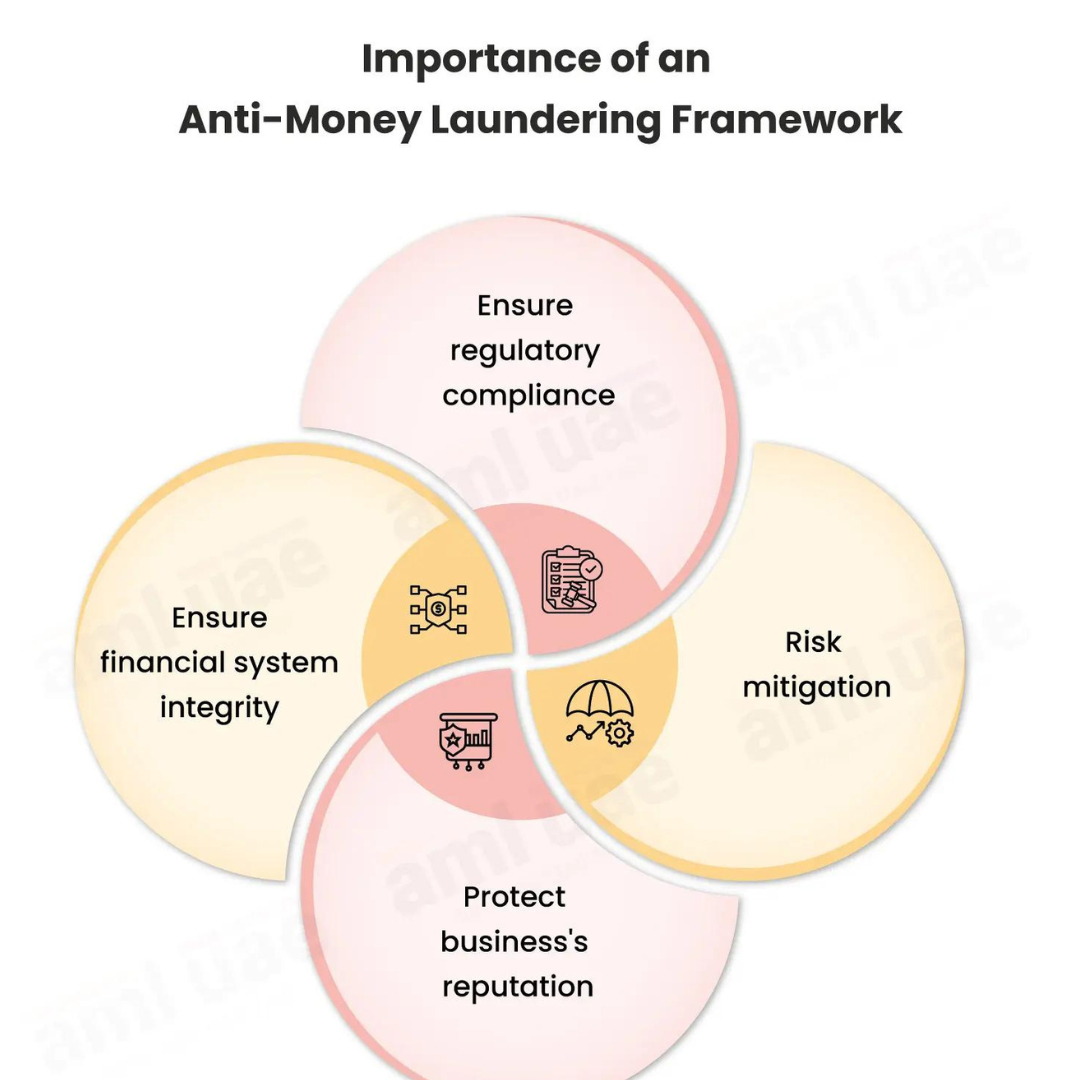
Money laundering poses significant threats to the integrity of financial systems and the broader economy. By facilitating illicit activities such as drug trafficking, terrorism, and corruption, money laundering undermines public trust, distorts markets, and compromises national security. Effective AML measures are essential for maintaining financial stability, protecting the reputation of financial institutions, and ensuring compliance with international standards.
The Role of Risk Monitoring in AML
Defining Risk Monitoring
Risk monitoring in the context of AML involves the continuous assessment of potential threats and vulnerabilities that may expose an organization to money laundering activities. It encompasses the identification, evaluation, and mitigation of risks to safeguard financial institutions from being exploited by criminals.

Key Components of Risk Monitoring
Transaction Monitoring
- Real-Time Analysis: Monitoring transactions in real-time to detect unusual patterns or behaviors that may indicate money laundering.
- Automated Systems: Leveraging advanced software and algorithms to identify and flag suspicious transactions for further investigation.

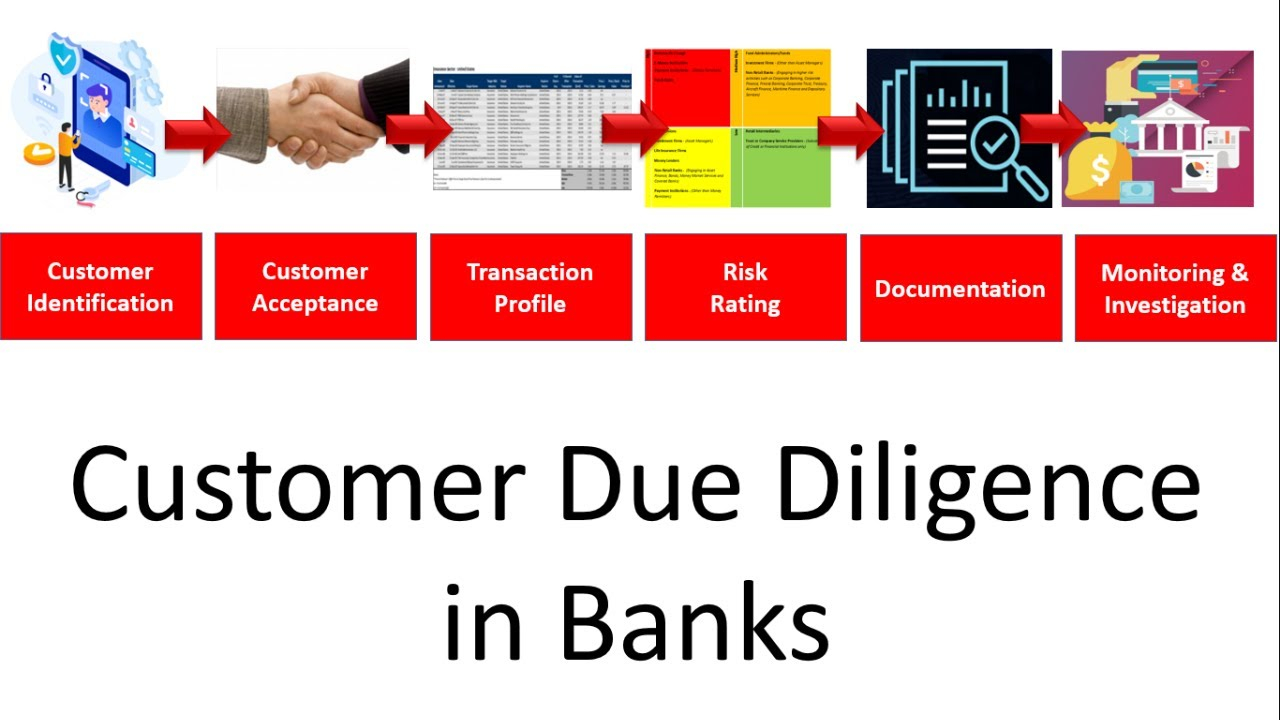
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
- Know Your Customer (KYC): Verifying the identity of customers and understanding their financial behavior to assess their risk profile.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously updating customer information and monitoring their transactions to detect any changes in risk levels.
Risk Assessment
- Risk-Based Approach: Implementing a risk-based approach to prioritize resources and efforts based on the level of risk posed by different customers and transactions.
- Periodic Reviews: Conducting regular risk assessments to adapt to evolving threats and regulatory requirements.

Reporting and Documentation
- Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs): Submit detailed reports on suspicious activities to relevant authorities as required by law.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining comprehensive records of transactions, customer information, and risk assessments to ensure transparency and accountability.

Importance of Risk Monitoring in AML
Early Detection of Threats
Effective risk monitoring enables financial institutions to identify and address potential money laundering activities at an early stage. By detecting suspicious transactions and behaviors in real time, organizations can prevent illicit funds from entering the financial system and mitigate the risk of regulatory penalties.
Enhanced Compliance
Regulatory authorities worldwide impose stringent AML requirements on financial institutions. Robust risk monitoring practices ensure compliance with these regulations, reducing the likelihood of fines, sanctions, and reputational damage. Compliance with AML standards also fosters trust among customers, investors, and stakeholders.

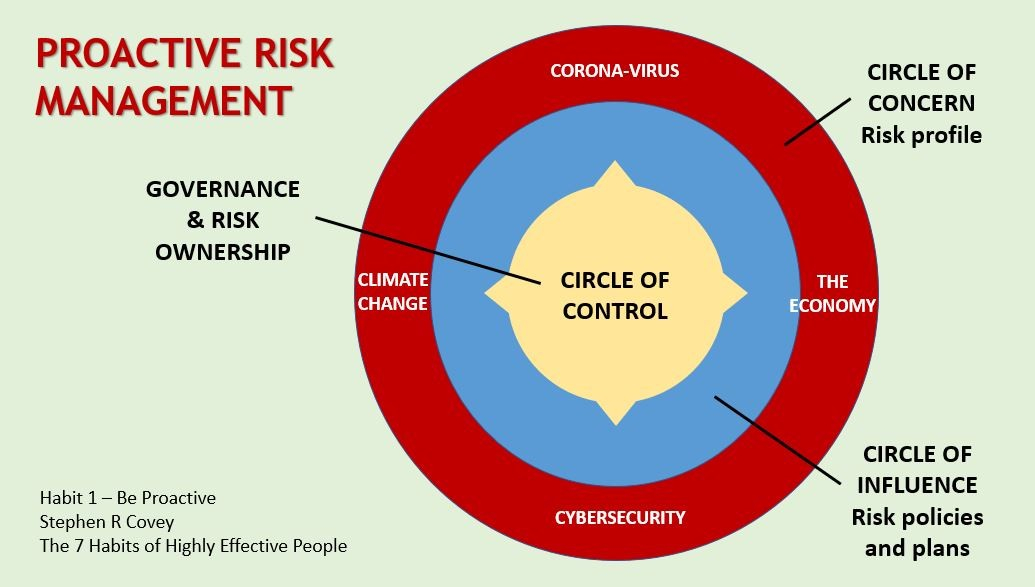
Proactive Risk Management
Risk monitoring empowers organizations to adopt a proactive approach to risk management. By continuously assessing and addressing emerging threats, financial institutions can stay ahead of criminals and adapt to evolving money laundering techniques. This proactive stance enhances the overall resilience of the organization.
Safeguarding Reputation
The reputation of a financial institution is one of its most valuable assets. Involvement in money laundering activities can severely damage an organization’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and business opportunities. Effective risk monitoring safeguards the institution's reputation by ensuring adherence to ethical standards and regulatory requirements.

Efficient Resource Allocation
Implementing a risk-based approach to AML allows financial institutions to allocate resources efficiently. By focusing efforts on high-risk areas and customers, organizations can optimize their compliance programs and achieve better outcomes with limited resources.

Supporting Law Enforcement
Financial institutions play a crucial role in supporting law enforcement agencies in the fight against money laundering. By monitoring and reporting suspicious activities, organizations provide valuable intelligence that aids investigations and prosecutions. This collaboration strengthens the overall AML framework and enhances the effectiveness of enforcement efforts.

Best Practices for Risk Monitoring in AML
Leverage Technology
Advanced technology solutions, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), can significantly enhance risk monitoring capabilities. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify complex patterns, and flag anomalies with greater accuracy and speed than traditional methods.

Implement Comprehensive Training Programs
Training employees on AML regulations, risk monitoring techniques, and emerging threats is essential for maintaining an effective compliance program. Regular training sessions ensure that staff members are equipped with the knowledge and skills to identify and respond to potential risks.

Foster a Culture of Compliance
Building a strong culture of compliance within the organization is crucial for effective risk monitoring. This involves promoting ethical behavior, encouraging open communication, and ensuring that all employees understand the importance of AML measures.
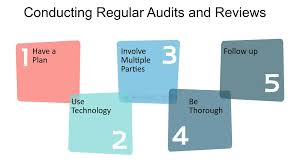
Conduct Regular Audits and Reviews
Regular audits and reviews of risk monitoring processes help identify gaps and areas for improvement. Independent assessments by internal or external auditors provide valuable insights and ensure that the organization’s AML program remains robust and up-to-date.
Collaborate with Industry Peers
Collaboration with other financial institutions, industry associations, and regulatory bodies enhances the effectiveness of risk monitoring efforts. Sharing best practices, intelligence, and resources fosters a collective approach to combating money laundering.

Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes
AML regulations are continually evolving in response to emerging threats and global trends. Staying informed about regulatory changes and adapting risk monitoring practices accordingly is essential for maintaining compliance and mitigating risks effectively.

Conclusion
Risk monitoring is a critical component of an effective AML program. By continuously assessing and addressing potential threats, financial institutions can safeguard their operations, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and protect their reputation. Leveraging advanced technologies, implementing comprehensive training programs, and fostering a culture of compliance are key strategies for enhancing risk monitoring capabilities. In an increasingly complex financial landscape, robust risk monitoring practices are essential for combating money laundering and maintaining the integrity of the global financial system.







.png)






